We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Our Policy.
DoorAccess
Standalone access
The essence of standalone is when the access point and processor is all on the door post.
Standalone is not high security if a door could be opened by breaking into wiring on the un-secured side of the door. Although most devices are standalone, and so low security, simple wiring and convenience makes them the most common access control.
Keypad
Probably the most common door access control, mostly for low security applications. Simple codes or PINs (personal ID numbers) are easily passed from person to person.


Card Access
Card access is more secure than keypads. A card or tag is required, but could be loaned. Some access controls use both card and PIN for extra security.


Other Access
Other personel access controls for doors and gates that qualify as standalone are....
Network access


Moving the processor to a secure area makes wiring more diffucult which can lead to reliability issues.
Controllers connect to any access point with a Wiegand standard output. That can include
- Keypads
- card readers
- QR readers
- Biometric readers
- Barcode readers
Mini controllers
Mini controllers serve two doors, or an in and out reader on the same door. Some versions are programmed through the access poiy, some are set via a WiFi connection.


Network controllers
Network controllers are controlled via a server, and potentially from an off site location. A laptop or desktop loaded with the editing tool connects to the network controller via TCP/IP. The database is held within the controller, so runs independantly.
- 2,4,or8 doors per controller using a shared database
- Secure admin editing, possibly via the cloud
- Local autonomous operation


Wiegand readers


Wiegand is a hardware and software data standard for an input device to connect to a controller.
There are several variations, the most important being data length. Most are 26 or 34 bits.
Wireless access
Access control devices have a smartphone app for editing, monitoring and to activate the internal relay.


Our popular K15 keypad has remote access variants i15 and K15t. The K15t has a network port that allows codes to be set via network cable, and relays activated remotely, including by smartphone.
GSM relay
FA.G64 relay has a network SIM to receive calls from a mobile phone or land line. When the call is received it activates the relay, then G64 drops the line so as not to incur a call charge.


G64 can be set "Any" caller or "Auth" callers. Any caller mode responds to all incoming calls. In 'Auth' mode, G64 reads the caller's ID, then only activates the relay for numbers stored. Two versions are available; with a 200 user or 1000 user ID memory.
The G64 can also send a text message to an 'admin' number each time it responds.
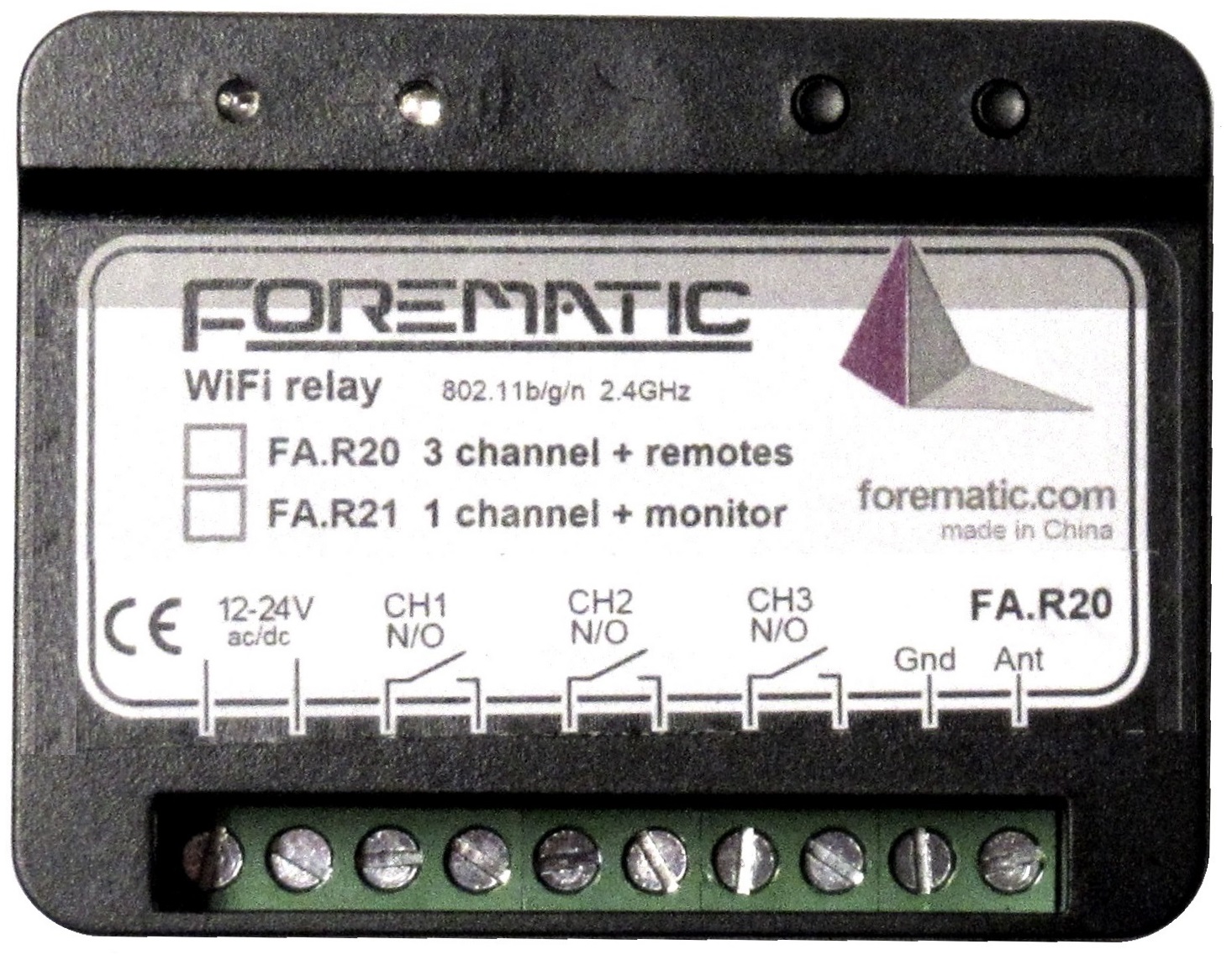
WiFi relay FA.R20 & FA.R21
Upload an ap to your smartphone and set a text on each button such as "open garage". R20 also has a learning radio receiver that works on 433MHz fixed code remotes and some rolling code remotes. The R21 variant has no radio receiver, but can monitor an input so that you can tell when the garage has been left open.

Video based access controls
As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes a standard feature in cameras, the processing power is employed to identify faces, finger prints, irises, and car number plates.
HRS Human Recognition Sensor
HR sensors are the first of a new class of devices using advanced video AI processing. HR sensors are taught Human the gait. Applications are intruder detection, and activation by humans only.
A unique application for the Human Recognition Sensor (HRS) is to monitor the area around an automated gate for human safety.


Facial Recognition Camera
A facial recognition camera stores facial data of each of the users. The realy output can activate a door or turnstile when the live face matches the data points stored.
Users naturally look up to the camera as they approach, as they did when their image was stored. The camera can store 500 users.


Numberplate Recognition
The ultimate vehicle recognition technology is NPR, because it identifies the vehicle, not the driver, or an ID device inside the vehicle.
NPR is accurate when it makes a positive ID, but some poor plates will come back with no positive ID. The security is underwritten by the state's intollerance of missing, damaged, or false plates.




